Iceland: A Unique Island Nation
Nestled in the North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland stands out as a remarkable island nation. Positioned between Europe and North America, this captivating land lies approximately 840 kilometers northwest of the United Kingdom and about 460 kilometers southeast of Greenland's shores. Its strategic location places Iceland just south of the Arctic Circle at the northern tip of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (MAR). Here, the convergence of the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates generates significant volcanic activity, making Iceland a fascinating destination for geology enthusiasts. Moreover, the nearest European lands are the Faroe Islands, situated a mere 530 kilometers away.
The Volcanic Heart of Iceland
Iceland boasts an impressive 30 active volcanic systems, with 14 having erupted since the island’s settlement in 874 AD. Remarkably, the latest eruption occurred on December 18, 2023, on Iceland's Reykjanes Peninsula, reminding us of the island's dynamic geological nature. Consequently, this constant volcanic activity contributes to Iceland's stunning landscape, characterized by raw natural beauty and breathtaking scenery. Thus, the island serves as a living showcase for volcanic phenomena. Visitors can explore geothermal areas, hot springs, and unique lava formations, which collectively create a captivating experience unlike any other.
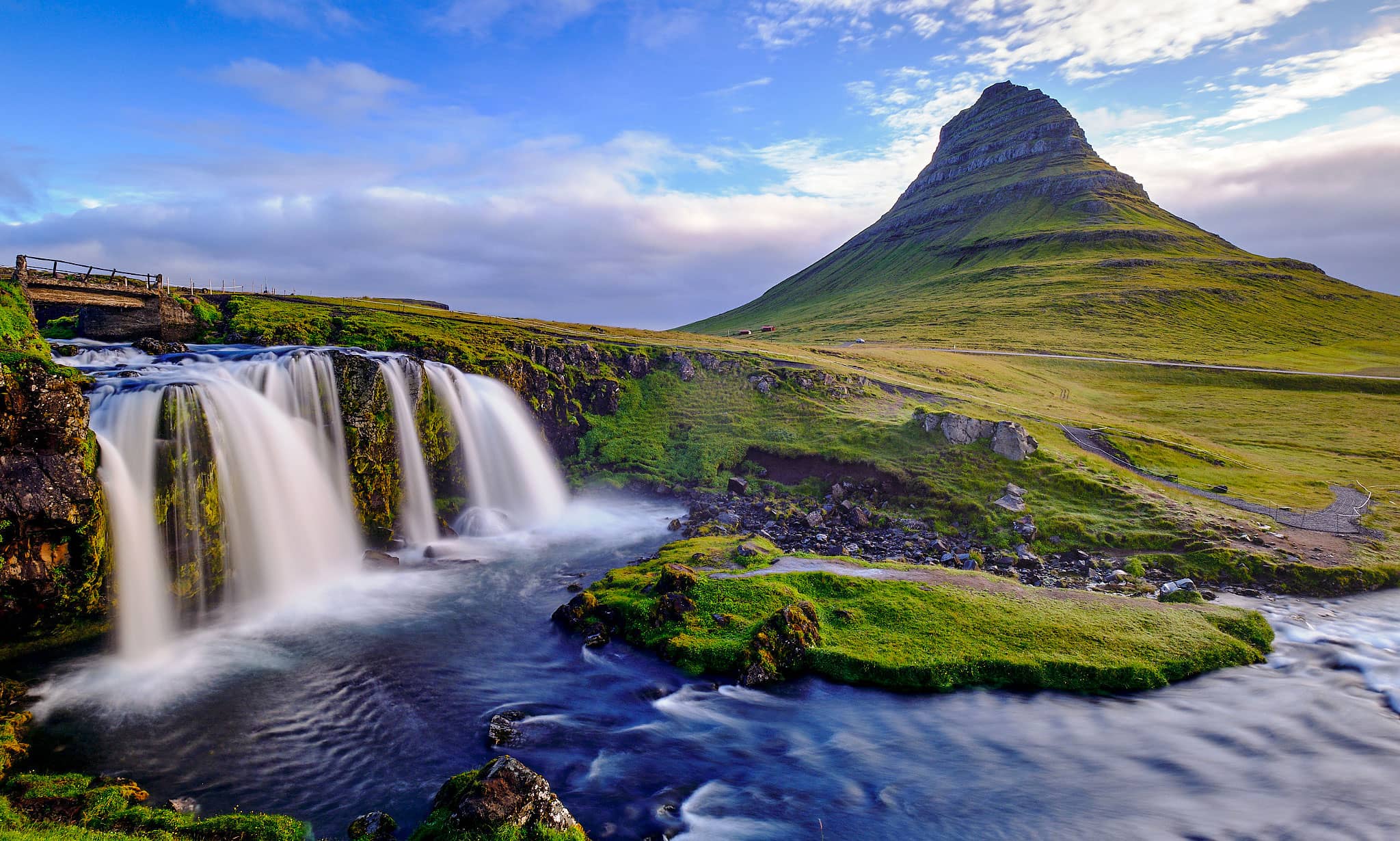
Stunning Landscapes
Covering an area of 103,000 square kilometers, Iceland is more than twice the size of Denmark or about the same size as the state of Kentucky in the United States. The country’s geography reveals an array of landscapes, featuring majestic fjords, sprawling glaciers, towering mountains, cascading waterfalls, and colossal lava fields. Furthermore, cold deserts and expansive tundras form an integral part of Iceland's allure. Despite its vast land area, only about 20-25 percent is habitable. Most of the population resides along the southern and eastern coasts, where the milder climate encourages settlement.
Population and Language
As of 2023, Iceland has a modest population of approximately 387,760 residents. This makes Iceland the least densely populated country in Europe, aside from Greenland. The capital city, Reykjavik, functions as the vibrant heart of Iceland, pulsating with culture and history. The predominant language spoken here is Icelandic, a member of the North Germanic languages, which reflects the rich cultural heritage of the island.
Historical Background of Iceland
Iceland's intriguing history began with the settlement of Norwegian and Celtic immigrants during the late 9th and early 10th centuries. Notably, Iceland is home to the world's oldest functioning legislative assembly, the Althing, which was established in 930 AD. This assembly marks a significant milestone in democratic governance, showcasing the island’s profound commitment to civic participation.
Colonial Influence and Independence
Although Iceland enjoyed over 300 years of independence, it eventually fell under the rule of Norway and subsequently Denmark. The late 19th century witnessed the catastrophic eruption of the Askja volcano in 1875, which severely impacted Iceland's economy, leading to widespread famine. This event drove approximately 20% of the island's population to emigrate, primarily toward Canada and the United States in search of better opportunities. Nevertheless, Iceland managed to reclaim its autonomy; it received limited home rule from Denmark in 1874 and ultimately achieved full independence in 1944. This journey towards self-governance reflects Iceland's resilience and determination.
Modern Iceland: A beacon of Excellence
Today, Iceland stands as a beacon of excellence in various social metrics. Notably, literacy, longevity, income, and social cohesion in the country rank among the highest in the world. Such achievements speak volumes about the commitment of Iceland's people to maintaining a high quality of life.
The Icelandic Government and Political Framework
Iceland operates as a constitutional republic characterized by a multi-party system. The government functions within a framework of parliamentary democracy, ensuring that every voice is heard. The Alþingi, or Parliament, plays a vital role in legislation, shaping the nation’s laws and policies. Importantly, Iceland prioritizes social welfare, environmental conservation, and economic stability, further emphasizing the collective values of its citizens. Most notably, the political landscape of Iceland showcases impressive diversity, allowing for various perspectives to contribute to the nation’s progress. Remarkably, Iceland has experienced enduring political stability, fostering a safe and secure environment for its residents.
Cultural Gems of Iceland
Iceland's rich cultural tapestry offers an exciting array of experiences. From traditional music festivals to vibrant art scenes, the nation celebrates its heritage with pride. Icelandic literature, notably the medieval sagas, reflects the country's storied history and captivating storytelling tradition. Visitors often find themselves drawn to events that showcase this unique culture, making every trip memorable.
Nature’s Masterpieces in Iceland
The natural wonders of Iceland truly deserve celebration. The Golden Circle, a popular tourist route, encompasses stunning sites like Þingvellir National Park, the Geysir Geothermal Area, and Gullfoss waterfall, showcasing nature's awe-inspiring beauty. Additionally, the Northern Lights, or Aurora Borealis, create a mesmerizing display, enchanting visitors during winter nights. Outdoor enthusiasts flock to the country for hiking, exploring glaciers, and witnessing volcanic landscapes, amplifying Iceland's reputation as an adventure destination.
In conclusion, Iceland emerges as a land of striking contrasts and extraordinary beauty. From its rugged landscapes and rich history to its commitment to social welfare and environmental sustainability, this island nation continues to capture the hearts and imaginations of all who visit. Thus, it stands not only as a remarkable destination but also as a testament to the indomitable spirit of its people.
Largest cities of: Iceland
| City Name | Population | Year of foundation | |
| Reykjavik | 131,136 | 874 | |
| Kopavogur | 35,935 | 1890 | |
| Hafnarfjordur | 29,045 | 874 | |
| Akureyri | 19,637 | 1786 | |
| Reykjanesbær | 19,414 | 1994 | |
| Gardabaer | 15,711 | 1972 | |
| Akranes | 7,332 | 1786 | |
| Ísafjörður | 2,633 | 1786 |
Iceland: Money