Discovering Rwanda: The Land of a Thousand Hills
Rwanda, often referred to as the "land of a thousand hills," is a relatively small nation nestled in Central Africa. Located south of the Equator and east of Lake Kivu, this landlocked country shares its borders with Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, and Uganda. With an area of approximately 26,338 square kilometers, Rwanda is similar in size to Macedonia or slightly smaller than the U.S. state of Maryland.
A Snapshot of the Population and Culture
As of 2016, Rwanda hosts a vibrant population of about 11.5 million people, making it one of the most densely populated countries in Sub-Saharan Africa. The capital and largest city, Kigali, is home to around 1 million residents. The official languages of Rwanda include Kinyarwanda, English, and French, while Swahili serves as a common lingua franca in the surrounding Great Lakes region. This linguistic diversity reflects the rich cultural tapestry of the nation.
A Tumultuous History
Rwanda's historical narrative witnessed a significant turning point in 1959 when the majority ethnic group, the Hutus, overthrew the ruling Tutsi monarchy. This event ignited a tragic series of conflicts, leading to the massacre of thousands of Tutsis and forcing around 150,000 individuals into exile. In the years that followed, these exiled Tutsis formed the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) and instigated a civil war that began in 1990. Consequently, ethnic tensions escalated, culminating in the horrific genocide of approximately 800,000 Tutsis and moderate Hutus in April 1994.
After the RPF triumphed over the Hutu government in July 1994, the violence finally ceased. However, about 2 million Hutu refugees fled Rwanda, fearing reprisals from the Tutsis. Many sought refuge in neighboring countries, including Burundi, Tanzania, Uganda, and what is now known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Over time, a significant number of these refugees returned to Rwanda, significantly transforming its demographic landscape.
Despite receiving substantial international support and implementing political reforms, including the nation’s first local elections in March 1999, Rwanda continues to face challenges. The struggle to increase investment and agricultural production, alongside fostering societal reconciliation, remains paramount. A history of large-scale population movements, ongoing threats from Hutu extremist insurgents, and military engagements in the Democratic Republic of Congo have further complicated these efforts.
The Geography of Rwanda
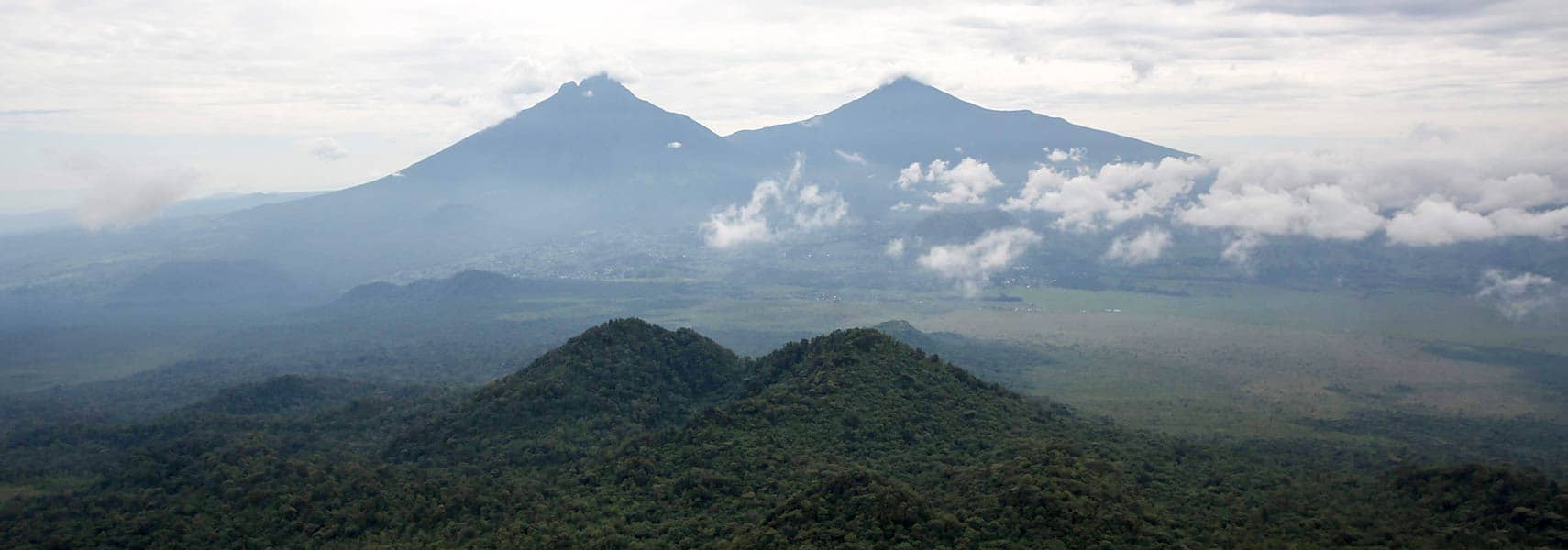
Geographically, Rwanda occupies a unique position in Central Africa, characterized by its diverse terrain. Stretching across 26,338 square kilometers, this nation boasts grasslands, rolling hills, and rugged mountains, particularly in the northwest where a chain of volcanoes exists. The highest point in Rwanda is the majestic Karisimbi Volcano, standing at 4,519 meters above sea level.
The climate in Rwanda remains mild and temperate, primarily due to its elevation. Interestingly, the country experiences two main rainy seasons each year, typically from February to April and again from November to January. These climatic conditions contribute to the lush landscapes and rich biodiversity that define Rwanda.
People and Culture in Rwanda
The nationality of the people reflects both unity and diversity, as Rwandans embrace a blend of ethnicities and cultures. The ethnic composition includes approximately 85% Hutu, 14% Tutsi, and 1% Twa. Notably, Christianity dominates the religious landscape, with 93.5% of the population identifying as Christians, while 4.6% practice Islam. A small fraction adheres to traditional African beliefs or claim no religious affiliation at all.
The country has a literacy rate of about 65%, highlighting the ongoing efforts to enhance education access in the region. Rwanda's commitment to improving literacy and education continues to be a driving force behind its development strategies.
Natural Resources and Agriculture
Rwanda's abundant natural resources significantly contribute to its economy. Gold, cassiterite (tin ore), and wolframite (tungsten ore) are among the valuable minerals found within its borders. Additionally, the country possesses accessible sources of methane, hydropower, and vast arable land suitable for agriculture.
Key agricultural products include coffee, tea, and pyrethrum (derived from chrysanthemums), as well as staples such as bananas, beans, and potatoes. The livestock sector further enhances the agricultural landscape, making it essential for food security and economic stability.
Economic Landscape and Industrial Sectors
The industries of Rwanda play a vital role in its economic framework. Major sectors include cement production, small-scale beverage manufacturing, and textiles. Other industries such as soap, furniture, shoes, plastics, and cigarettes also contribute to the national economy.
When it comes to exports, Rwanda primarily relies on commodities like coffee, tea, and hides, alongside tin ore. The Democratic Republic of the Congo stands as Rwanda’s largest export partner, accounting for nearly 19.8% of total exports. Other significant partners include the United States, China, and Swaziland.
Conversely, the country imports various goods, including foodstuffs, machinery, and petroleum products. Uganda, Kenya, and India make up the largest sources of imports, indicating an interconnected economic environment within the region.
Rwanda's Path Towards Progress
In recent years, Rwanda has made remarkable strides towards rebuilding and advancing its national identity following past conflicts. The emphasis on reconciliation, economic development, and environmental sustainability illustrates Rwanda's unique position in Central Africa today. By embracing innovation and fostering a spirit of unity, Rwanda aspires to secure a prosperous future for its citizens.
The journey toward recovery and growth continues to inspire many around the world. In summary, Rwanda stands as a testament to resilience, illustrating how a nation can rise from adversity and work towards a brighter tomorrow.
Largest cities of: Rwanda
| City Name | Population | Year of foundation | |
| Kigali | 1,200,000 | 1907 | |
| Butare | 60,000 | 1912 | |
| Gisenyi | 50,000 | 1934 | |
| Musanze | 44,000 | 2000 | |
| Rubavu | 40,000 | 1960 | |
| Ruhango | 30,000 | 1962 | |
| Nyagatare | 25,000 | 1959 | |
| Kirehe | 20,000 | 2000 |
Rwanda: Money